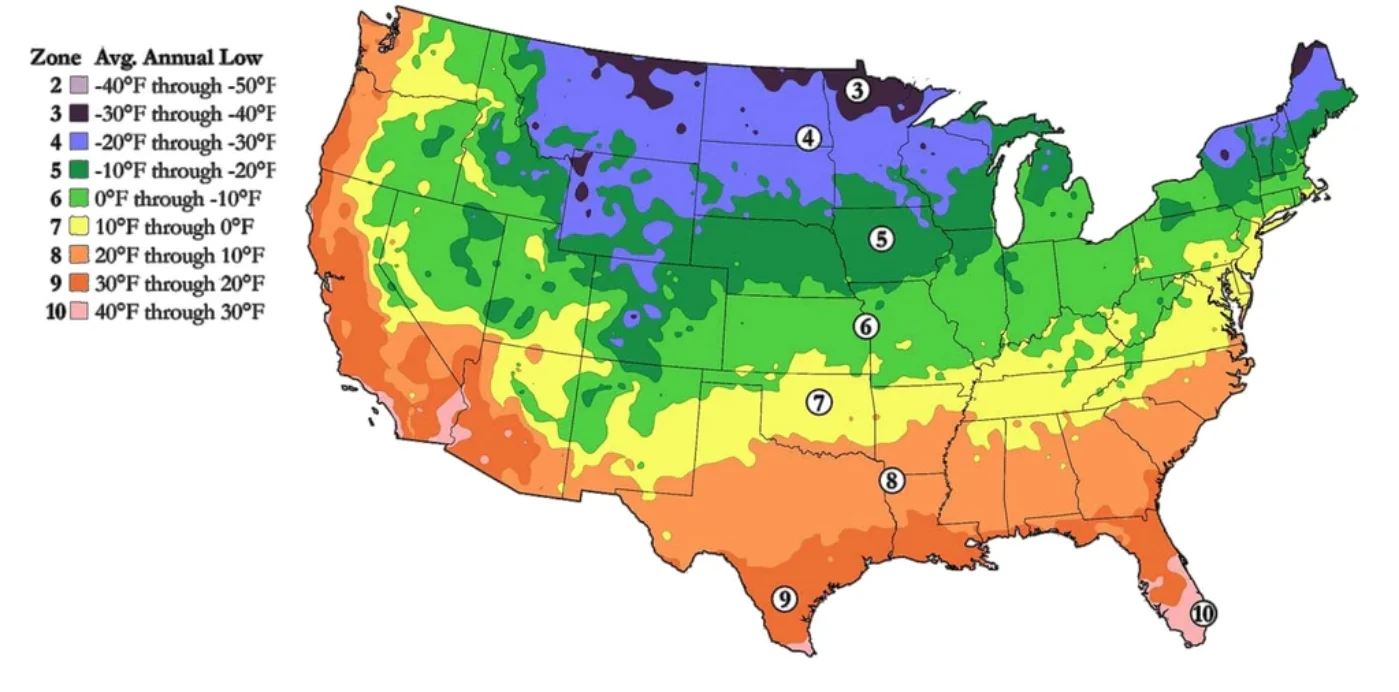
Various microclimates shape each region’s gardening potential in California. Rather than just looking at zone designations, identifying your area’s authentic climate personality will help you select plants naturally tailored to thrive. Estimate the amount and severity of precipitation. Observe the effects of rainfall on the plants in your garden. Frequent dry spells indicate drought defiance shapes regional choices. Review heat and cold records for your zone. Sustained peaks and valleys require specific adaptations. Know your zone’s temperature comfort range.
Higher elevations and southern zones see more intense sun while coastal areas experience heavy fog. Measure sunlight hours and UV index in your garden. Note exposure variations. Analyze wind velocity averages and storm frequency. Identify prevailing wind direction. Exposed, windy zones demand sturdy, well-anchored plants. Storm-prone regions benefit from flexible natives with good water tolerance. Research your zone’s predominant soil types. Test garden soil pH, nutrients, and salinity levels. Certain zones share key soil similarities that shape appropriate plants. Note what thrives wild in preserves near your zone. Study their structural adaptations. Replicate favorable conditions for these plants in your garden. Talk to experienced gardeners in your area about your zone’s defining climate influences. Review references documenting your zone’s precipitation, temperatures, sunlight, wind, and soil qualities. Compare against on-site findings.
- Creating your weather journal to record temperature fluctuations, precipitation, and storm events over an entire year provides helpful insights into your zone’s seasonal personalities.
- Consulting heat zone maps in addition to planting hardiness zones gives further insight into the high-temperature thresholds that plants endure in your region.
- Photographing and cataloging native species during site visits to natural areas ensures you remember their habitat preferences to replicate in your zone garden.
- Talking to vendors at local nurseries frequented by seasoned area gardeners guide plant varieties well-suited to your zone’s hyperlocal conditions.
- Situating weather tracking instruments like thermometers and wind gauges in your garden for a full year reveals detailed data on local climate patterns.
- Joining online regional gardening forums and groups allows exchanging insights with fellow zone inhabitants to reinforce your climate knowledge.
- Closely monitoring how current garden plantings fare provides clues about microclimate factors like sunlight, drainage, and wind flow.
- Having soil samples from different California planting zone areas professionally lab tested provides comprehensive data on pH, nutrient levels, and composition.
- Consulting the heat zone maps published by the American Horticultural Society provides additional guidance on the high heat thresholds plants withstand in your zone.
- Creating illustrated maps of your property noting variations in sunlight, wind flow, hardscapes, and vegetation helps reveal the diverse microclimates within your zone.
Paying attention to how water flows and pools in your landscape after rains reveal important drainage insights that impact plant choices. Maintaining a digital photo journal documenting your garden’s seasonal progression gives visual evidence of your zone’s timing for bloom periods, leaf emergence, and dormancy. Joining Facebook groups focused on California gardening allows you to exchange insights and ask questions to hundreds of fellow regional gardeners. Conducting percolation tests across your property determines water retention and permeability rates of your soil for plant selection.







